Products Introduction
Uncalibrated Phase Delay
We use GREAT software for multi-GNSS EWL/WL/NL UPD estimation and product generation.
Basic Observables: For GPS/Galileo/BDS, triple-frequency carrier phase and code observations from 106 reference stations from IGS and MGEX networks are used (GPS: L1/L2/L5 Galileo: E1/E5a/E5b BDS: B1/B2/B3). For GLONASS, L1/L2 observations from 124 reference stations with receiver TRIMBLE NETR9 are used.
Data Preprocessing: Preprocessing of the GNSS data to determine geometry-free (GF) & Melbourne-Wubbena (MW) cycle slip, remove outliers and eliminate short arcs.
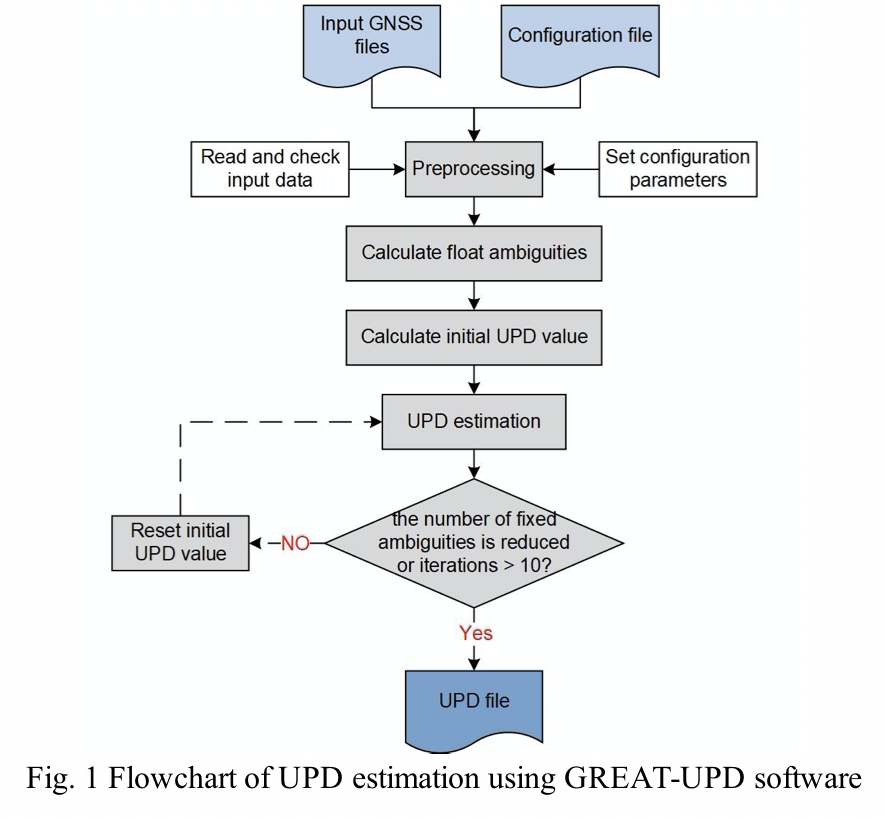
UPD Estimation Methodology: Figures 1 shows the flowchart of UPD estimation. The procedure for UPD estimation can be divided into three steps:
First, calculate the float ambiguities. For EWL/WL UPD estimation, the float EWL/WL ambiguities can be formed from HMW combination, with DCB (and IFCB) correction. For NL UPD estimation, the float NL ambiguities can be calculated based on the restored integer WL ambiguities and the estimated IF ambiguities.
Second, obtain the initial UPD values based on the float ambiguities. Firstly, set the receiver UPD of one station with the largest number of visible satellites to zero, and calculate the UPD of each satellite observed by this station. For the next station with common satellites, its UPD can be calculated by averaging the fraction parts of ambiguities from which the satellite UPDs are removed. If the other satellites can be observed by this station, corresponding satellite UPDs can be calculated based on the receiver UPD. After obtaining UPDs of all stations, we recalculate the satellite UPD by averaging the fraction parts of ambiguities from which the receiver UPDs are removed. After iterating the above steps three times, the initial UPD values of all stations and satellites are obtained.
Third, select a reference satellite to eliminate the rank deficiency and then the least square estimator is conducted iteratively to generate UPDs of all stations and satellites. After each iteration, the number of ambiguities that can be fixed will be counted. If the number of the fixable ambiguities decreases or the number of iterations is greater than 10, the iteration is stopped. The condition for judging whether the ambiguity can be fixed is: after the removal of satellite and station UPDs, the ambiguity is considered as fixed when its fraction is less than the threshold (0.25 cycles).
Naming Format:
upd_ewl_YYYYDOY_GEC - Daily extra-wide-lane UPD of GPS, Galileo and BDS constellations
upd_wl_YYYYDOY_GREC - Daily wide-lane UPD of GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and BDS constellations
upd_nl_YYYYDOY_GREC - Daily narrow-lane UPD at 30-sec intervals of GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and BDS constellations
File Format:
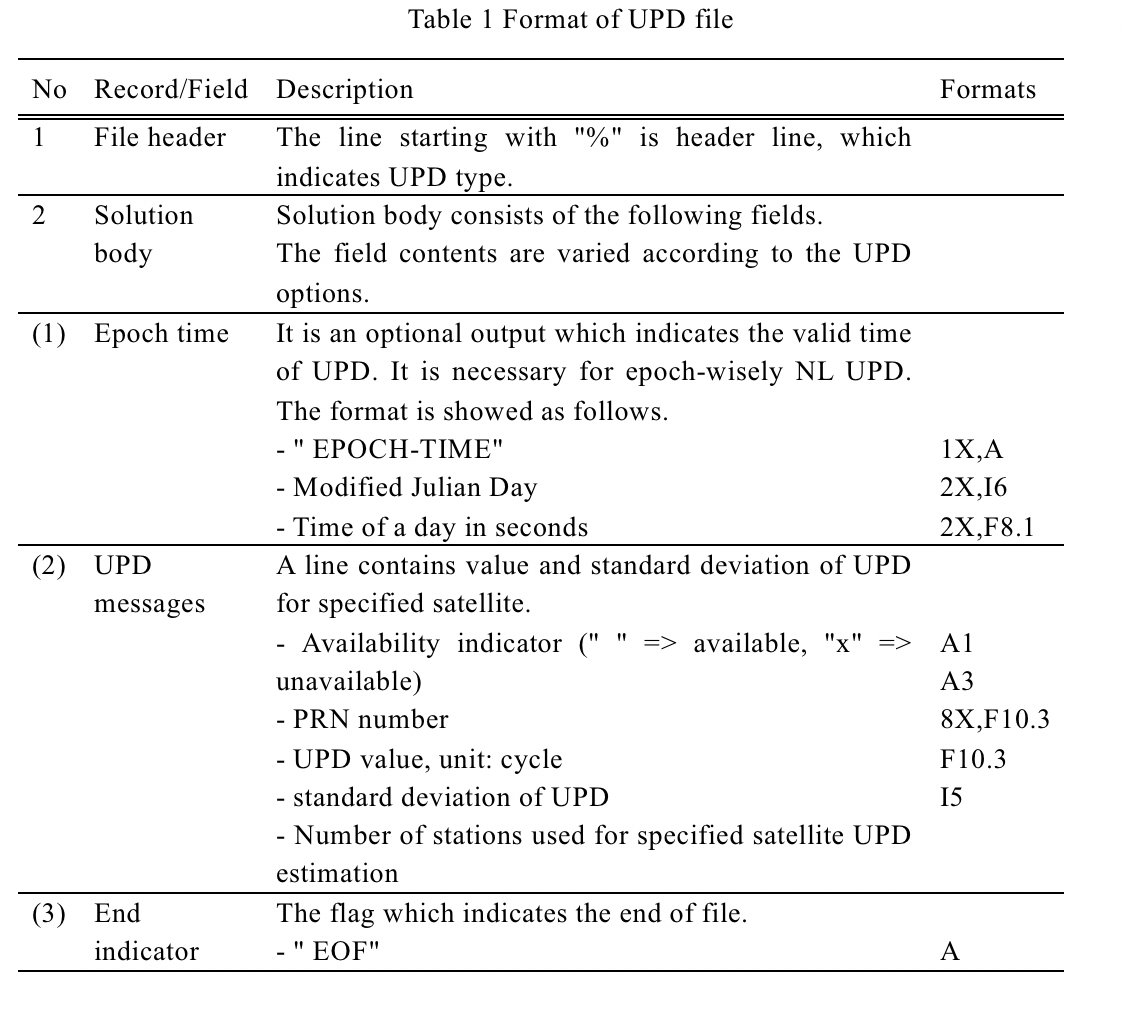
UPD file is just a text file containing EWL/WL/NL UPD records. A line indicates a UPD record of specified satellite. The following table shows the format of the UPD file.