Innovation Center
iGMAS Innovation Center: backgrounds and goals
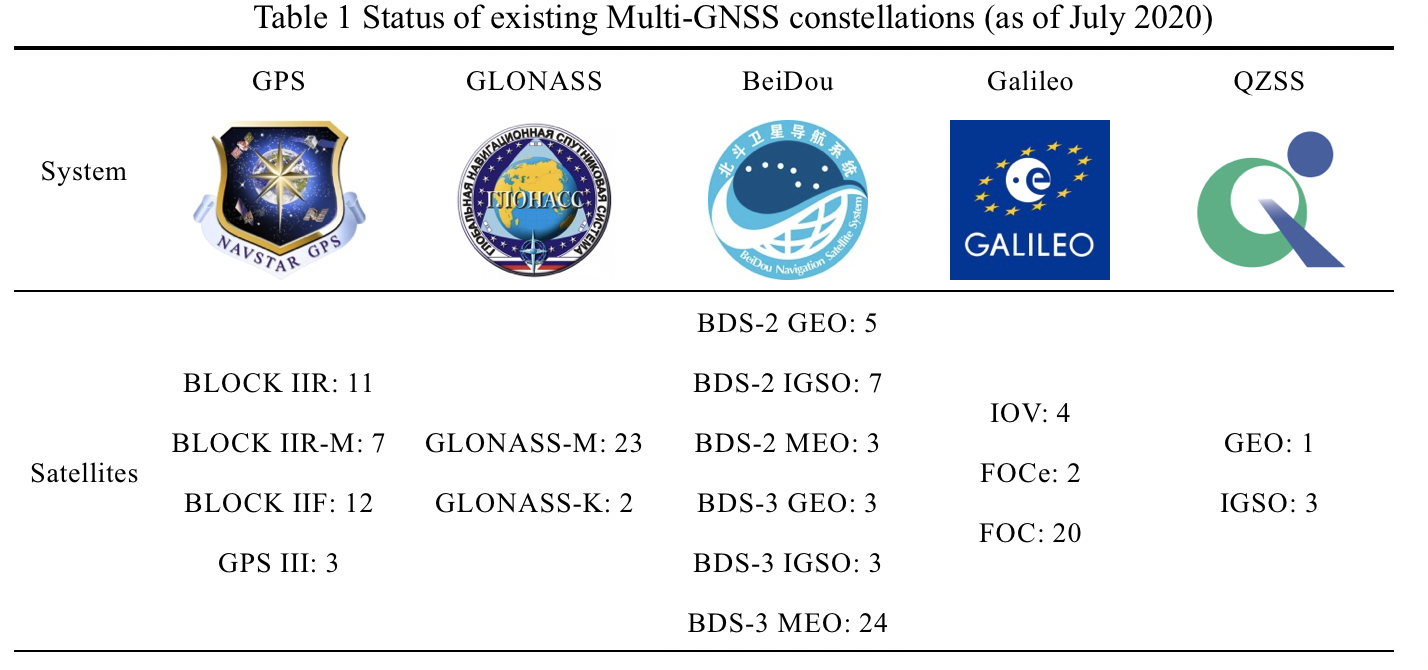
As the official commissioning of the global BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS-3) was announced on July 31, China has become the third country in the world to independently own a global navigation satellite system. As of July 2020, 124 satellites from GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and BDS are available to provide navigation service for global users. Moreover, the new-generation GNSS satellites such as GPS Block IIF/III, GLONASS-K, BDS-2/BDS-3 and Galileo satellites all operate on three or more frequencies. With the availability of multi-GNSS and multi-frequency observations, the performance of positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) services is expected to be further improved in the near future.
In order to monitor the operational status and evaluate the performances of each GNSS, China has initiated the International GNSS Monitoring and Assessment System, or commonly known as “iGMAS”, in 2007. As of July 2020, iGMAS consists of a global network with 30 multi-GNSS stations, 3 data centers, 12 analysis centers , 1 monitoring and evaluation center, 1 product combination center, and 1 operation control center. Besides reporting the systems’ operational status and evaluating the service performances, iGMAS also generates high-precision GNSS products including satellite orbits, satellite clock offsets, Earth rotation parameters (ERPs), station coordinates and velocities, and global ionosphere maps (GIMs).
Enormous new application fields such as autonomous vehicles, the Internet of Things (IOT), and intelligent robot, etc., make new demands on the real-time, high-precision and reliability of GNSS. For example, the real-time clock products are essential to real-time precise positioning. Moreover, it is already well-known that un-differenced ambiguity resolution will greatly improve the accuracy and reliability of GNSS precise point positioning (PPP). However, the ambiguities cannot be fixed to integers unless the un-differenced uncalibrated phase delay (UPD) products are available. Unfortunately, multi-GNSS real-time satellite clock products and UPD products are not yet provided by iGMAS. As a result, current iGMAS products must be updated and enriched.
In addition, low Earth orbit (LEO) constellation has now become a new research hotspot and is vital to the future of satellite industry and scientific applications. OneWeb, SpaceX, Boeing and other internationally renowned companies have announced ambitions for their respective constellations with hundreds or thousands of LEO satellites. Although these LEO constellations are being proposed to deliver broadband Internet services globally, they also have the potential to operate as navigation system. Enormous researches have explored how to leverage these commercial constellations for navigation and examined the full system architecture, including satellites’ geometric distribution, signal in space user ranging errors, the onboard chip-scale atomic clocks as well as the orbit determination methods. The results are optimistic and indicate that the navigation based on LEO constellation is feasible in the way of protecting, toughening and augmenting services. Moreover, LEO constellation would also help to improve the accuracy of GNSS precise orbit determination in the combined POD solution, especially for the satellites in geostationary orbits. LEO constellation can also contribute to global atmosphere monitoring and terrestrial reference frame realization. With these advantages, LEO constellations may also be a part of the next generation BeiDou system (BDS-4).
In this context, we have decided to establish iGMAS innovation center. The main goals of iGMAS innovation center are:
(1) to improve the accuracy and reliability of existing BDS/GNSS products such as precise orbits and clocks, and to further enrich iGMAS products such as UPDs and integer recovery clocks;
(2) to study theoretical and practical foundations, and to develop models and algorithms for LEO-augmented GNSS technologies. The main research focus will include LEO-augmented GNSS PPP, integrated precise orbit determination, LEO-GNSS meteorology and ionospheric sounding methodology, terrestrial reference frame realization, etc.;
(3) to expand the service areas of iGMAS to support scientific and engineering applications. For example, iGMAS innovation center will provide precise science orbit products for GRACE (and GRACE Follow-on) and Swarm satellites, which could be helpful for modeling Earth’s gravity field and understating geomagnetic field.